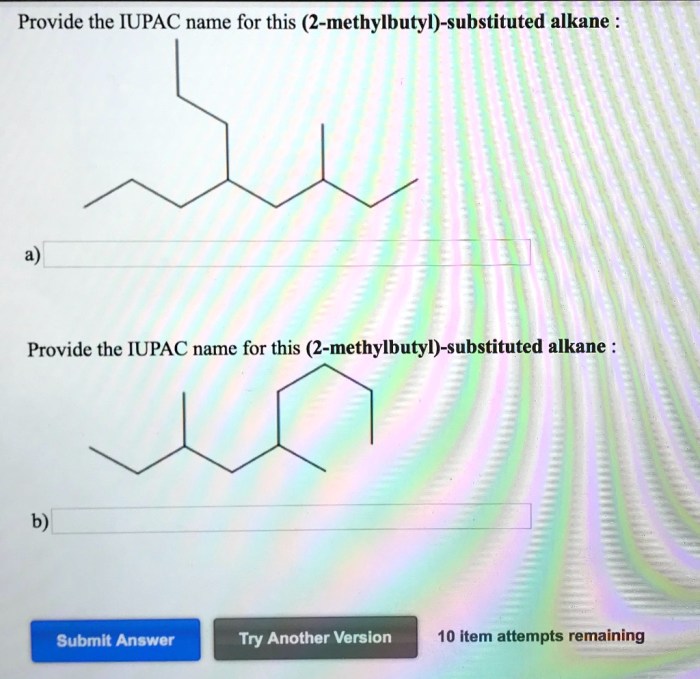
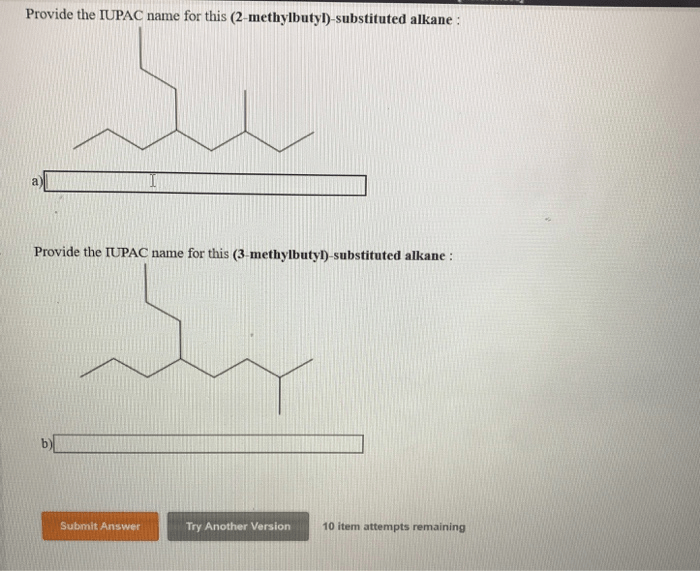
Provide the iupac name for this 3 methylbutyl substituted alkane – In the realm of organic chemistry, the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) nomenclature system reigns supreme, providing a standardized language for naming organic compounds. This article delves into the intricacies of IUPAC nomenclature, specifically focusing on the task of assigning the precise name to 3-methylbutyl substituted alkanes.
Join us as we navigate the rules and conventions that govern the naming of these branched hydrocarbons, unraveling the systematic approach that ensures clarity and consistency in chemical communication.
The systematic naming of alkanes, a class of saturated hydrocarbons, follows a set of well-defined rules established by IUPAC. These rules take into account the number of carbon atoms in the parent chain, the presence and position of any substituents, and the type of substituents attached to the parent chain.
Understanding these rules is crucial for accurately naming 3-methylbutyl substituted alkanes, ensuring effective communication among chemists and researchers.
Introduction

The IUPAC name for the 3-methylbutyl substituted alkane is 3-methylbutane. The IUPAC naming system for alkanes is based on the number of carbon atoms in the parent chain and the type and position of any substituents.
Alkanes are a class of saturated hydrocarbons that contain only carbon and hydrogen atoms. They are characterized by their single bonds between carbon atoms and their lack of functional groups.
IUPAC Nomenclature
The rules for naming alkanes with substituents are as follows:
- The parent chain is the longest continuous chain of carbon atoms in the molecule.
- Substituents are named by changing the ending of the alkane name to -yl.
- The position of the substituent is indicated by a number.
- Multiple substituents are named in alphabetical order.
For example, the IUPAC name for the alkane with a methyl substituent on the third carbon atom is 3-methylbutane.
3-Methylbutyl Substituted Alkane
The parent alkane for the 3-methylbutyl substituted alkane is butane.
The methyl substituent is located on the third carbon atom of the parent chain.
Therefore, the IUPAC name for the 3-methylbutyl substituted alkane is 3-methylbutane.
Physical and Chemical Properties
3-Methylbutane is a colorless liquid with a boiling point of 60 °C and a melting point of -118 °C.
It is a flammable liquid that is insoluble in water.
3-Methylbutane is a relatively unreactive compound.
Applications, Provide the iupac name for this 3 methylbutyl substituted alkane
3-Methylbutane is used as a solvent and as a fuel.
It is also used in the production of other chemicals, such as isobutylene and methacrylic acid.
FAQ Overview: Provide The Iupac Name For This 3 Methylbutyl Substituted Alkane
What is the IUPAC nomenclature system?
The IUPAC nomenclature system is a standardized set of rules and conventions established by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) for naming inorganic and organic compounds.
How do I name 3-methylbutyl substituted alkanes using IUPAC nomenclature?
To name 3-methylbutyl substituted alkanes using IUPAC nomenclature, identify the parent alkane, determine the position of the methyl substituent, and use the appropriate prefixes to indicate the number and position of substituents.
What are the physical and chemical properties of 3-methylbutyl substituted alkanes?
The physical and chemical properties of 3-methylbutyl substituted alkanes vary depending on the size and structure of the parent alkane and the position of the methyl substituent. These properties include boiling point, melting point, density, reactivity, and stability.