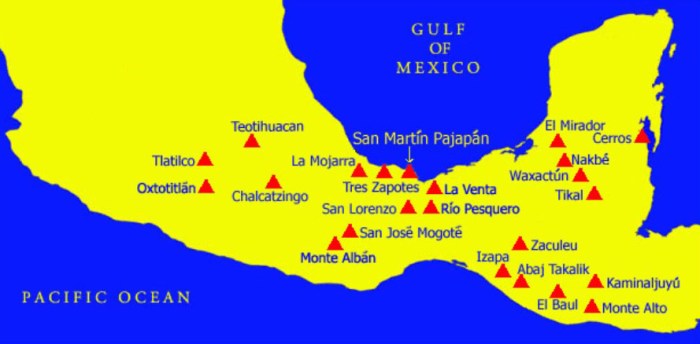
Regional states in ninth-and tenth-century mesoamerica – In the dynamic tapestry of Mesoamerican history, the regional states that emerged in the ninth and tenth centuries played a pivotal role, shaping the political, cultural, and economic landscape of the region. This article delves into the complexities of these states, examining their origins, interactions, and eventual decline.
During this period, Mesoamerica witnessed the rise of powerful regional states, each with its unique characteristics and sphere of influence. From the Maya city-states of the southern lowlands to the Zapotec kingdom of Monte Albán, these states engaged in complex political and military interactions, leaving an enduring mark on Mesoamerican history.
Mesoamerican Regional States in the Ninth and Tenth Centuries: An Overview

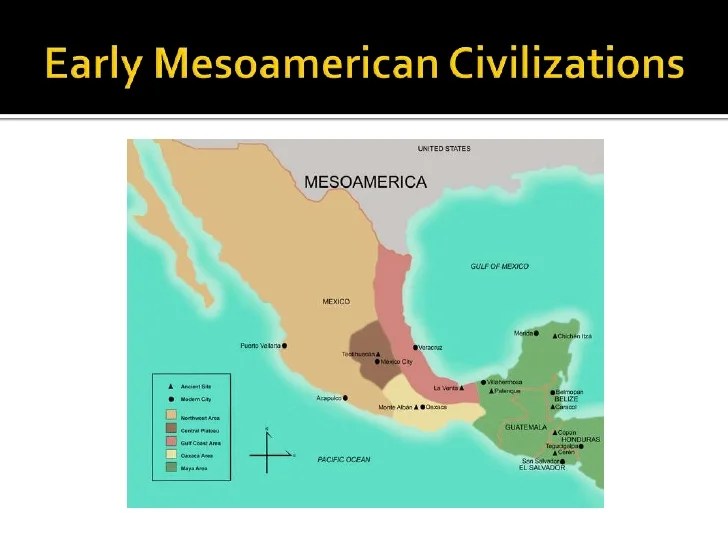
Regional states emerged in Mesoamerica during the ninth and tenth centuries, marking a significant period of political and cultural transformation. Mesoamerica, a region encompassing present-day Mexico and Central America, was home to diverse civilizations that developed complex political systems and cultural traditions.
The ninth and tenth centuries witnessed the rise of powerful regional states, each controlling vast territories and exercising political influence over neighboring areas. These states played a pivotal role in shaping the political landscape of Mesoamerica, engaging in interactions and conflicts that influenced the region’s history.
Major Regional States in Ninth- and Tenth-Century Mesoamerica
Several major regional states emerged in Mesoamerica during this period:
- Maya: Located in present-day southern Mexico and northern Central America, the Maya civilization was renowned for its advanced writing system, calendar, and mathematical knowledge.
- Teotihuacan: Located in central Mexico, Teotihuacan was a major urban center that exerted political and cultural influence over a vast region.
- Zapotec: Based in the Oaxaca Valley of southern Mexico, the Zapotec civilization was known for its complex political organization and architectural achievements.
- Toltec: Located in central Mexico, the Toltec state emerged in the tenth century, inheriting the legacy of Teotihuacan and influencing the political landscape of Mesoamerica.
Interactions and Conflicts between Regional States, Regional states in ninth-and tenth-century mesoamerica
The regional states of Mesoamerica engaged in a range of interactions and conflicts that shaped their political and social landscapes:
- Political Alliances: States formed alliances to strengthen their positions and counterbalance rivals.
- Trade and Commerce: Extensive trade networks connected different regions, facilitating the exchange of goods and ideas.
- Military Conflicts: Territorial disputes and political ambitions often led to armed conflicts between states.
- Cultural Exchange: Interactions between states led to the exchange of cultural practices, beliefs, and technologies.
FAQ Corner: Regional States In Ninth-and Tenth-century Mesoamerica
What were the major regional states in ninth- and tenth-century Mesoamerica?
Some of the major regional states during this period included the Maya city-states of Tikal, Calakmul, and Chichén Itzá, as well as the Zapotec kingdom of Monte Albán and the Teotihuacan empire.
How did these states interact with each other?
Regional states engaged in a range of interactions, including political alliances, trade, warfare, and cultural exchange. These interactions shaped the political landscape of Mesoamerica and influenced the development of each state.
What factors contributed to the decline of regional states in the late ninth and tenth centuries?
Various factors, such as environmental changes, political instability, and external pressures, are believed to have contributed to the decline of regional states. These factors led to the collapse of some states and the emergence of new powers.