Embark on an extraordinary journey with The Space Race Answer Key, where we unravel the fascinating tale of human ambition and scientific prowess. From the origins of this epic rivalry to its profound impact on our understanding of the cosmos, this guide holds the key to unlocking the secrets of space exploration.
Join us as we delve into the technological breakthroughs, international rivalries, and scientific discoveries that shaped the Space Race, leaving an enduring legacy on humanity’s quest for knowledge and the stars.
Historical Context

The space race emerged as a consequence of the Cold War rivalry between the United States and the Soviet Union. Both nations sought to demonstrate their technological prowess and ideological superiority by achieving milestones in space exploration.
Key figures in the space race included Soviet Premier Nikita Khrushchev, who initiated the Sputnik program, and US President John F. Kennedy, who challenged the nation to land a man on the Moon by the end of the 1960s. Organizations such as NASA in the US and the Soviet Space Agency played crucial roles in advancing space technology and executing ambitious missions.
Sputnik Crisis
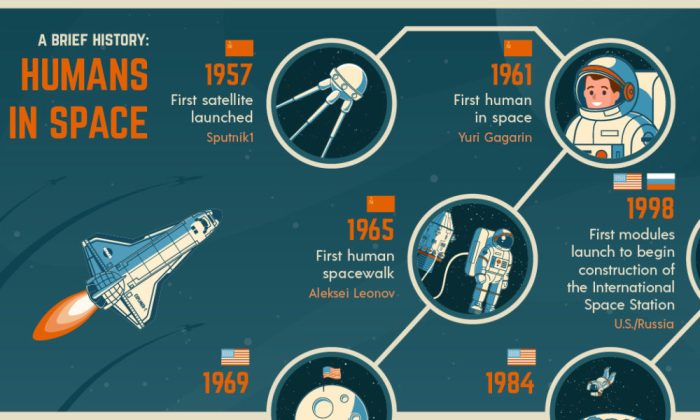
The launch of Sputnik 1, the first artificial satellite to orbit Earth, by the Soviet Union in 1957 triggered the Sputnik crisis. This event sparked concerns in the US about the technological gap with the Soviets and led to increased investment in space research and education.
Technological Advancements
The space race sparked a surge of innovation, leading to groundbreaking technological advancements in various fields. These breakthroughs revolutionized scientific research, space exploration, and human spaceflight.
Spacecraft and Rockets
- Sputnik 1:The first artificial satellite launched by the Soviet Union in 1957, marking the beginning of the space race.
- Apollo 11:The spacecraft that carried the first humans to the Moon in 1969.
- Space Shuttle:A reusable spacecraft used by NASA from 1981 to 2011 for various space missions.
- International Space Station:A modular space station in low Earth orbit, continuously inhabited by astronauts and cosmonauts since 2000.
Other Innovations
- Computers:The development of computers and microelectronics played a crucial role in controlling spacecraft, processing data, and enabling communication with Earth.
- Materials Science:The need for lightweight and durable materials for spacecraft led to advancements in metallurgy, composites, and ceramics.
- Robotics:Remote-controlled robots were used for various tasks in space, such as satellite servicing and space exploration.
These technological advancements significantly enhanced scientific research by enabling the study of space and its phenomena from new perspectives. They also expanded human spaceflight capabilities, allowing astronauts to explore farther and stay longer in space.
International Rivalries and Collaborations
The space race was a period of intense competition between the United States and the Soviet Union for supremacy in space exploration. This rivalry was driven by both ideological and strategic factors. The United States saw space exploration as a way to demonstrate its technological superiority and to promote its democratic values.
The Soviet Union, on the other hand, saw space exploration as a way to boost its international prestige and to prove the superiority of its communist system.Despite the intense competition, there were also instances of cooperation between the two superpowers.
Delving into the depths of the space race answer key can be a mind-boggling experience. But let’s take a break from the cosmic complexities and shift our focus to the synthesis of an alum lab. This fascinating process involves the creation of a beautiful crystalline compound with unique properties.
Learn more about the synthesis of an alum lab and then return to unravel the mysteries of the space race answer key with renewed enthusiasm.
In 1975, the United States and the Soviet Union launched the Apollo-Soyuz mission, which saw an American spacecraft dock with a Soviet spacecraft in orbit. This mission was a major milestone in space exploration and demonstrated the possibility of cooperation between the two countries.
Impact of International Tensions and Alliances on Space Exploration Efforts
The space race was also influenced by international tensions and alliances. The Cold War between the United States and the Soviet Union created a climate of mistrust and suspicion, which made it difficult for the two countries to cooperate on space exploration.
However, the United States was able to form alliances with other countries, such as the United Kingdom and Canada, which helped it to pool its resources and expertise in space exploration.
Examples of Joint Projects or Collaborations between Different Nations
In addition to the Apollo-Soyuz mission, there have been other examples of joint projects or collaborations between different nations in space exploration. For example, the International Space Station (ISS) is a joint project between the United States, Russia, Canada, Japan, and the European Space Agency.
The ISS is a modular space station that has been continuously inhabited since 2000 and has served as a platform for a wide range of scientific research and technological development.
Scientific Discoveries and Explorations
The space race fueled a surge of scientific discoveries and explorations, forever altering our understanding of the cosmos. Lunar missions, planetary probes, and space telescopes unveiled hidden wonders, revolutionizing our knowledge of the solar system and beyond.
Lunar Missions, The space race answer key
- Apollo 11 (1969): First human moon landing, bringing back lunar samples and revealing the moon’s barren surface.
- Apollo 15-17 (1971-1972): Collected more lunar samples, deployed scientific instruments, and explored the moon’s highlands and valleys.
- Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter (2009-present): Orbits the moon, mapping its surface and searching for potential resources.
Planetary Probes
- Mariner 4 (1965): First close-up images of Mars, revealing its cratered surface and thin atmosphere.
- Viking 1 and 2 (1976): Landed on Mars, conducted experiments, and searched for signs of life.
- Voyager 1 and 2 (1977): Explored the outer planets, providing stunning images of Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune.
Space Telescopes
- Hubble Space Telescope (1990-present): Revolutionized astronomy, capturing deep-space images and providing insights into the early universe.
- James Webb Space Telescope (2022-present): Successor to Hubble, with enhanced capabilities to observe distant galaxies and the formation of stars and planets.
Societal and Cultural Impact: The Space Race Answer Key
The space race ignited a global fascination with science and technology, inspiring countless individuals to pursue careers in STEM fields. It led to the development of innovative technologies that have revolutionized various industries, including communications, materials science, and medicine.
Education and Public Interest in Science
The space race sparked an unprecedented interest in science education. Governments invested heavily in STEM programs, leading to the establishment of new schools, universities, and research institutions. This increased focus on science and technology education inspired a generation of scientists, engineers, and astronauts who went on to make significant contributions to space exploration and other fields.
Role of the Media
The media played a pivotal role in shaping public perceptions of the space race. Newspapers, magazines, and television broadcasts captivated audiences with thrilling accounts of rocket launches, lunar landings, and scientific discoveries. This extensive coverage not only informed the public but also fostered a sense of national pride and international competition.
Expert Answers
What were the major technological advancements of the Space Race?
The Space Race spurred groundbreaking advancements in rocketry, spacecraft design, and space exploration technologies, including the development of the Saturn V rocket, the Apollo spacecraft, and the Hubble Space Telescope.
How did the Space Race contribute to scientific discoveries?
The Space Race led to numerous scientific discoveries, including the first lunar landing, the discovery of the Van Allen radiation belts, and the exploration of other planets in our solar system, expanding our knowledge of the cosmos.
What was the impact of the Space Race on society and culture?
The Space Race had a profound impact on society, inspiring technological advancements, education, and public interest in science. It also influenced popular culture, with space-themed movies, TV shows, and music becoming widely popular.